Data Analytics
Data Analytics: Unveiling Insights from Data
Data analytics refers to the process of examining, cleaning, transforming, and interpreting data to discover meaningful patterns, insights, and trends. It involves the application of statistical, mathematical, and computational techniques to data with the goal of making data-driven decisions, solving problems, and gaining a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Importance of Data Analytics
Informed Decision-Making: Data analytics empowers organizations to make informed, evidence-based decisions, leading to improved outcomes and efficiency.
Competitive Advantage: It provides a competitive edge by uncovering insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency.
Risk Mitigation: Identifying risks and opportunities in advance allows organizations to proactively manage potential challenges.
Innovation: Data analytics fuels innovation by revealing emerging patterns and customer preferences.

FAQ
The main goals are to gain insights from data, make informed decisions, identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and improve overall business performance.
Data analytics focuses on examining historical data to extract insights, while data science encompasses a broader scope, including data analytics, machine learning, and predictive modeling.
Data anonymization, consent management, adherence to privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR), and ethical data usage guidelines are essential.
The Data Analytics Process
Data Collection: Gathering data from diverse sources, which can include databases, sensors, surveys, and web scraping.
2. Data Preprocessing: Cleaning and transforming the data to ensure data quality, addressing issues like missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies.
3. Data Exploration: Initial analysis through summary statistics, data visualization, and exploratory data analysis (EDA) to understand the data’s characteristics.
4. Data Analysis: Applying various analytical techniques to uncover patterns, relationships, and insights within the data.
5. Data Interpretation: Drawing meaningful conclusions and insights from the analysis, often with the aim of answering specific questions or solving problems.
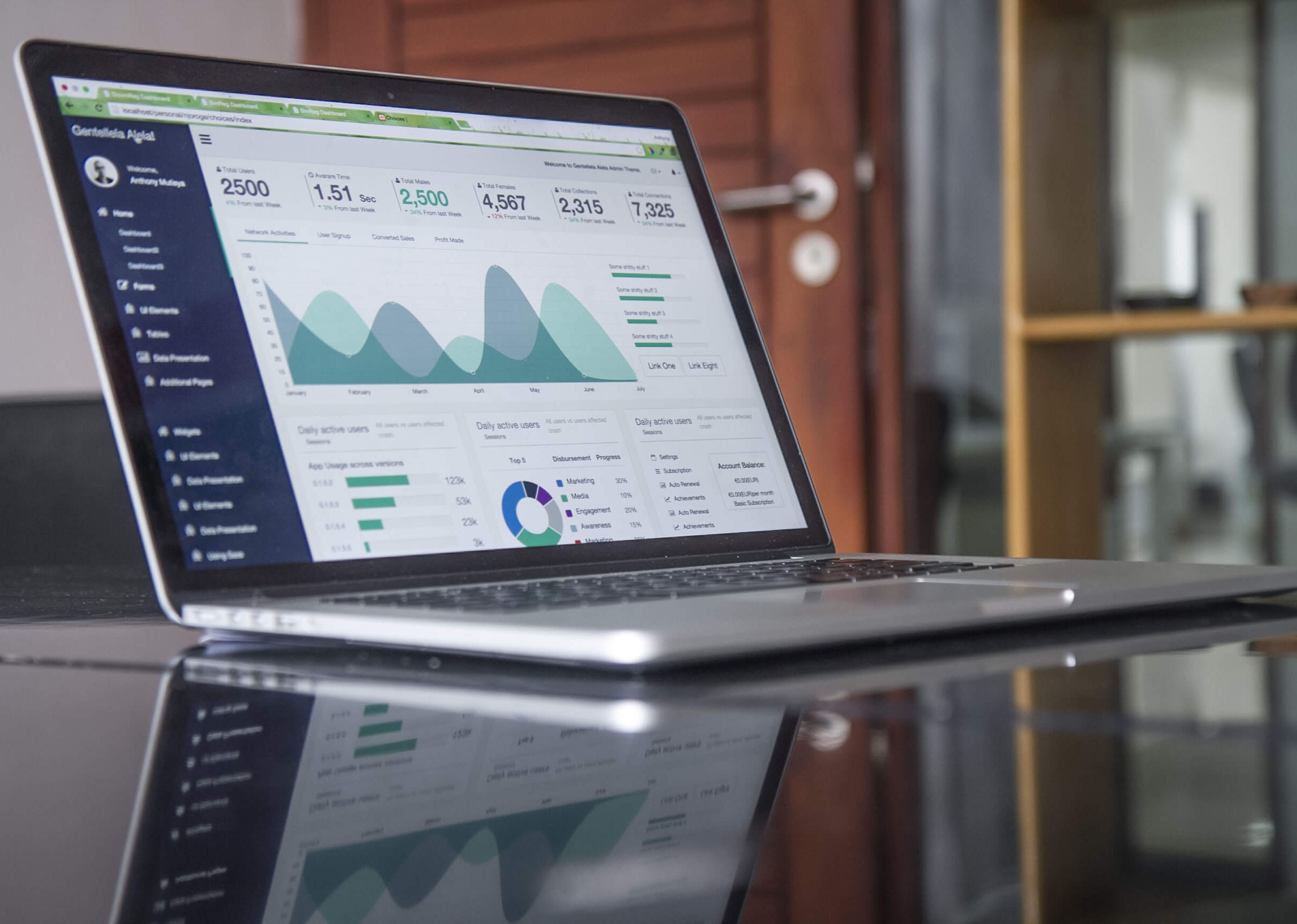
6. Data Visualization: Presenting findings using charts, graphs, and visual representations to facilitate understanding and communication.
7. Reporting and Decision-Making: Communicating the results to stakeholders and using data-driven insights to guide strategic decisions and actions.
